Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) is a kind of long bone fracture specially used in children. It is characterized by small trauma and minimally invasive operation, which does not affect the child’s bone development, and has little impact on the healing of the fracture and the child’s future bone development. So It is God’s gift to Children.

How did ESIN come about?
The classical approach to the treatment of fractures in children paid particular attention to orthopedic treatment. The bone remodeling capacity in children corrects residual deformations through growth, while the classical methods of osteosynthesis may entail many complications. However, these opinions are not always confirmed by facts. Spontaneous bone remodeling is subject to rules referring to the fracture site, the type and degree of displacement, and the age of the patient. When these conditions are not met, osteosynthesis is needed.
The technical procedures that are currently available for the treatment of adults cannot be applied to children. Plate osteosynthesis requires extensive periosteal stripping, in conditions in which the periosteum plays an essential role in the consolidation of fractures in children. Intramedullary osteosynthesis, with the penetration of the growth cartilage, induces endosteal circulation disorders and severe growth problems, because of epiphysiodesis or growth stimulation through the complete obstruction of the medullary canal. In order to eliminate these inconveniences, elastic intramedullary nailing has been designed and used.
Basic Principle Introduction
The working principle of elastic intramedullary nail (ESIN) is to use two intramedullary nails made of titanium alloy or stainless steel with good elastic recovery to be inserted symmetrically from the metaphysis. Each elastic interlocking nail has three support points on the inside of the bone. The elastic restoring force of the elastic nail converts the thrust and pressure required for fracture reduction through the 3 contact points of the medullary cavity.
The elastic intramedullary nail is C-shaped, which can accurately locate and build an elastic system that resists deformation, and has sufficient stability for the movement of the fracture site and partial load-bearing.
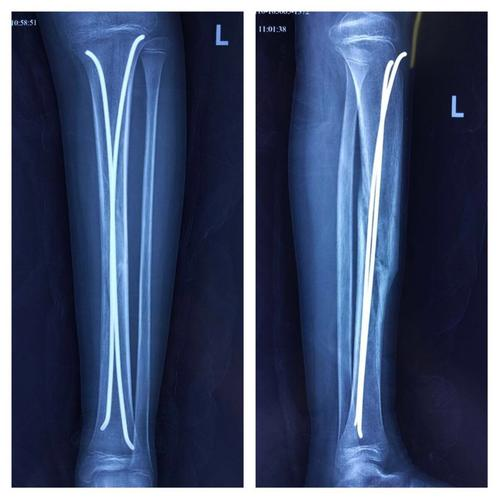
Major Advantage-Biological Stabilities
1) Flexural stability
2) Axial stability
3) Lateral stability
4) Anti-rotational stability.
Its biological stability is the basis for obtaining the desired therapeutic effect. Therefore, It’s good choice to do elastic intramedullary nails fixation.
Applicable symptoms
The clinical indications for ESIN TENS are usually based on the patient’s age, fracture type, and location.
Age range: Generally, the age of patients is between 3 and 15 years old. The upper age limit can be appropriately increased for thin children, and the lower age limit can be appropriately lowered for obese children.
Intramedullary nail diameter and length selection: The size of the nail depends on the diameter of the medullary cavity, and the diameter of the elastic nail = the diameter of the medullary cavity x 0.4. The selection of straight elastic intramedullary nails generally follows the following rules: 3 mm in diameter for 6-8 years old, 3.5 mm in diameter for 9-11 years old, and 4 mm in diameter for 12-14 years old. In the case of diaphyseal fracture, the length of the elastic nail = the distance from the needle insertion point to the contralateral growth plate + 2 cm. The optimal length of the elastic needle should be equal to the distance between the growth plates on both sides, and 2-3 cm of the needle should be reserved outside the bone for future extraction.
Applicable fracture types: transverse fractures, spiral fractures, multi-segment fractures, bifocal fractures, short oblique or transverse fractures with wedge-shaped fragments, long fractures with cortical support, pathological fractures caused by juvenile bone cysts.
Applicable fracture sites: femoral shaft, distal femoral metaphysis, proximal femoral subtrochanteric area, calf diaphysis, distal calf metaphysis, humeral diaphysis and subcapital area, humerus supra-ankle area, ulna and radius diaphysis, Radial neck and radial head.
Contraindications:
1. Intra-articular fracture;
2.Complex forearm fractures and lower extremity fractures without any cortical support, especially those who need to bear weight or are older, are not suitable for ESIN.
The operation points:
The first step in fracture reduction is to use external devices to achieve closed reduction of the fracture.
Subsequently, an elastic intramedullary nail of appropriate length and diameter is selected and bent into the appropriate shape.
Finally, the elastic nails are implanted, when two elastic nails are used in the same bone, the elastic nails should be symmetrically plasticized and placed to obtain better mechanical balance.
In conclusion, elastic intramedullary nailing is a very effective treatment for fractures of school-age children, which can not only perform biologically minimally invasive fixation and reduction of fractures, but also does not increase the risk of complications.
Post time: Mar-18-2022
