Suture anchors help doctors attach soft tissues, like tendons or ligaments, to bone during orthopedic surgery. You may hear about them most in surgeries with small cuts, called arthroscopic surgery. These small tools are important for holding soft tissue in place. They help make recovery smoother and more dependable. Many people ask if suture anchors are safe and work well. Doctors use them because they give strong support and last a long time. After surgery, your doctor will check your healing and help you recover.
Key Takeaways
Suture anchors attach soft tissue to bone. This helps you heal faster and feel less pain after surgery. These devices let doctors make smaller cuts. Smaller cuts mean less harm to your body and faster healing. Suture anchors have different types. Some do not break down, and some do. Each type works best for certain surgeries. New suture anchor technology makes surgery safer and better. It also helps surgeries go faster and lowers problems. Always ask your doctor which suture anchor is best for you. Follow your doctor’s advice to heal well.
Suture Anchors Overview
What Are Suture Anchors
You might ask what suture anchors are and why doctors use them in orthopedic surgery. Suture anchors are small devices that help connect soft tissue, like tendons or ligaments, to bone. Surgeons use these anchors in many surgeries, especially when they need to fix torn tissue back to where it belongs. Suture anchors have changed how doctors repair injuries. They let doctors make quick and strong connections between tissue and bone.
Suture anchors have three main parts:
The Anchor: This part goes inside the bone. It can look like a screw or a tiny plug. Doctors pick anchors made from metal or special materials that can dissolve.
The Eyelet: This is a hole or loop in the anchor. The suture goes through the eyelet, linking the anchor to the suture.
The Suture: This is a tough thread that connects the tissue to the anchor. Surgeons use different kinds of suture, some stay in the body and some dissolve.
Tip: Suture anchors help doctors fix injuries with smaller cuts. This means less pain and quicker healing for you.
Suture anchors work well in many joints, like the shoulder, knee, and ankle. Their design helps doctors make a strong spot on the bone. This strong link helps your tissue heal in the right place.
How Suture Anchors Work
If you have an injury that needs surgery, your doctor may use suture anchors to fix it. The surgeon puts the anchor into the bone near the torn tissue. The suture goes through the eyelet and then through the tissue. The doctor ties the suture to pull the tissue close to the bone. This keeps the tissue in place while it heals.
Suture anchors let surgeons use less invasive methods. These ways use smaller cuts, so your body has less trauma and you recover faster. For example, in shoulder surgery, suture anchors help attach the rotator cuff tendon to the bone. This lets you get movement and strength back sooner.
Here is how suture anchors help in orthopedic surgery:
They make a strong and stable link between soft tissue and bone.
They let doctors use smaller cuts, so you feel less pain and heal faster.
They help surgeons do repairs quickly and safely.
They lower the chance of long-term problems by keeping tissue in the right spot.
Doctors use suture anchors in many surgeries. For example, they treat shoulder injuries, knee ligament tears, and some hand and foot problems. Suture anchors give results like other repair methods, such as transosseous sutures. Both ways help bring back movement and strength, and the risk of problems is low.
Note: Suture anchors have made surgery better by making repairs more reliable and helping you heal faster.
Suture anchors keep getting better. New designs make them stronger and easier to use. Some anchors have low profiles, so they do not stick out from the bone. This helps lower irritation and helps you heal faster. Surgeons now have more choices, so they can pick the best anchor for your injury.
If you need orthopedic surgery, suture anchors may help you recover. They let your doctor fix your injury with less pain and help you get back to normal activities faster.
Types of Suture Anchor Devices

There are many kinds of suture anchor devices. Each kind helps doctors attach soft tissue to bone in its own way. XC Medico has many suture anchor devices for different needs. You can count on their quality and new ideas.
Non-Absorbable Anchors
Non-absorbable suture anchor devices stay in your body after surgery. Doctors use them when you need support for a long time. These anchors are made from titanium or stainless steel. They are often used in shoulder or knee repairs. Non-absorbable anchors hold tissue tightly, but they can make future surgeries harder.
Here is a table that shows how non-absorbable and biodegradable suture anchors are different:
Type of Suture Anchor | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Non-absorbable | Lasts a long time, many material choices | Can loosen, harder to fix with another surgery |
Absorbable | Easier to redo, no need to remove, better for the body | May cause swelling or other reactions |
PEEK Corded Anchors
PEEK corded suture anchor devices use a strong plastic called Polyether-Ether-Ketone. This plastic is tough and gentle on your tissue. Doctors like PEEK anchors because they do not show up on X-rays. They also cause less trouble in your body. PEEK anchors are used for rotator cuff repairs. Studies show PEEK anchors work well, even if bone changes happen near them.
Evidence Summary | Findings |
Study Focus | Compared PEEK anchors to other non-metal anchors in rotator cuff repair |
Key Finding | Bone changes near PEEK anchors do not change how well they work |
Clinical Scores | ASES and Constant scores got better, no matter the bone changes |
Conclusion | PEEK anchors work well for rotator cuff repairs, even with bone changes |
Knot-Free Anchors
Knot-free suture anchor devices help doctors finish surgery faster. You do not need to tie knots to keep the suture in place. This makes surgery quicker and lowers the chance of problems. Knot-free anchors work for many injuries. Research shows knot-free anchors work as well as knotted ones and help you heal safely.
Study Reference | Findings | Outcome Measures |
Benca et al | Knot-free and knotted anchors are both strong | N/A |
Safran et al | Knot-free anchors moved very little under normal use | N/A |
Rhee et al | Results were the same after two years | N/A |
Maldonado et al | Patients felt much better after two years | PROMs got better |
General finding | Surgery is faster and there are fewer problems | N/A |
Tip: Ask your doctor about biodegradable suture anchors if you want one that dissolves over time.
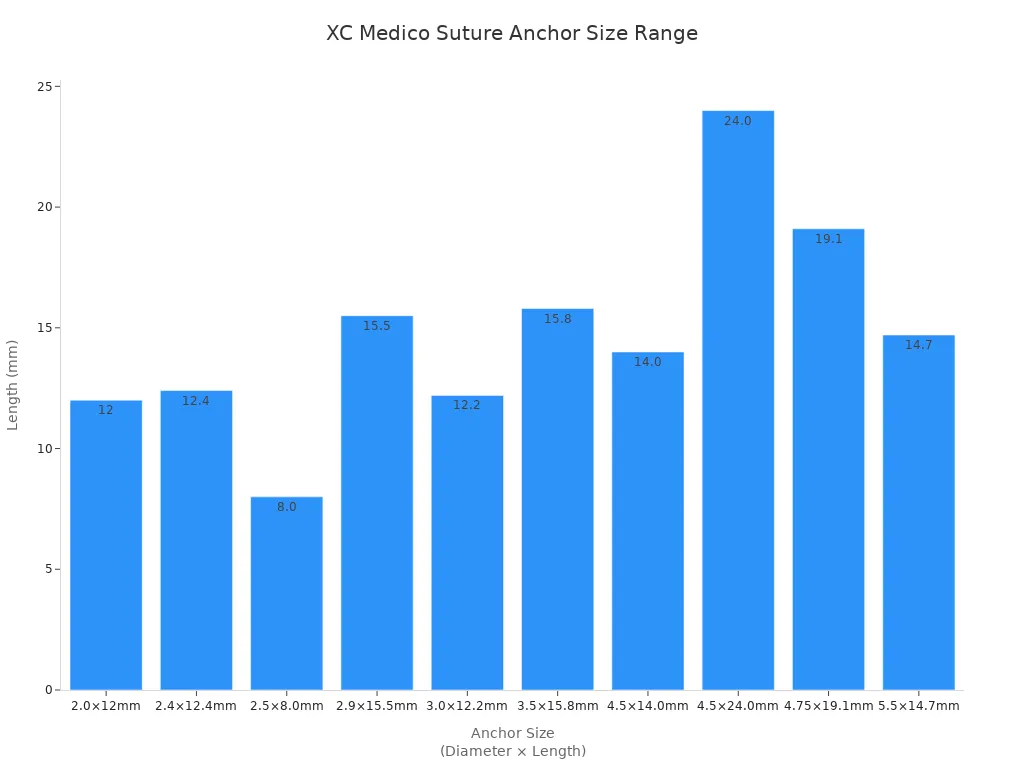
Suture anchor devices come in many sizes and materials. XC Medico has preloaded shoulder suture anchor devices made from PEEK or titanium alloy. You can find the right suture anchor device for your injury and trust that it is safe.
Suture Anchors in Orthopedic Surgery
Common Procedures
If you hurt your shoulder, tear a ligament, or damage a tendon, you might need suture anchors. Doctors use these devices in many surgeries. Arthroscopic surgery uses suture anchors because it needs smaller cuts. This means you feel less pain. Suture anchors are used a lot in rotator cuff repairs, shoulder stabilization, and knee ligament repairs.
Many patients get much better after surgery:
Most people move better and feel less pain.
Some groups can move their arm 31° more.
People get stronger after surgery.
Most do not have another tear.
Doctors see strong tendons in 75% of cases.
Only 4% of people have another tear after rotator cuff repair.
Suture anchors help you heal faster. You can return to your normal life sooner. These devices help you recover and feel better.
Securing Soft Tissue to Bone
Suture anchors are important for fixing tendons to bone. In arthroscopic surgery, the doctor puts the anchor into the bone. The suture goes through the anchor and attaches to your tissue. This keeps the tissue in the right place while it heals.
Suture anchors are made from strong materials like titanium or special plastics. The threads on the anchor help it stay in the bone. Strong suture material helps the doctor hold the tissue tight. This way, there is less harm to other areas. You can heal faster.
Tip: Suture anchors make repairs stronger and help you move again sooner.
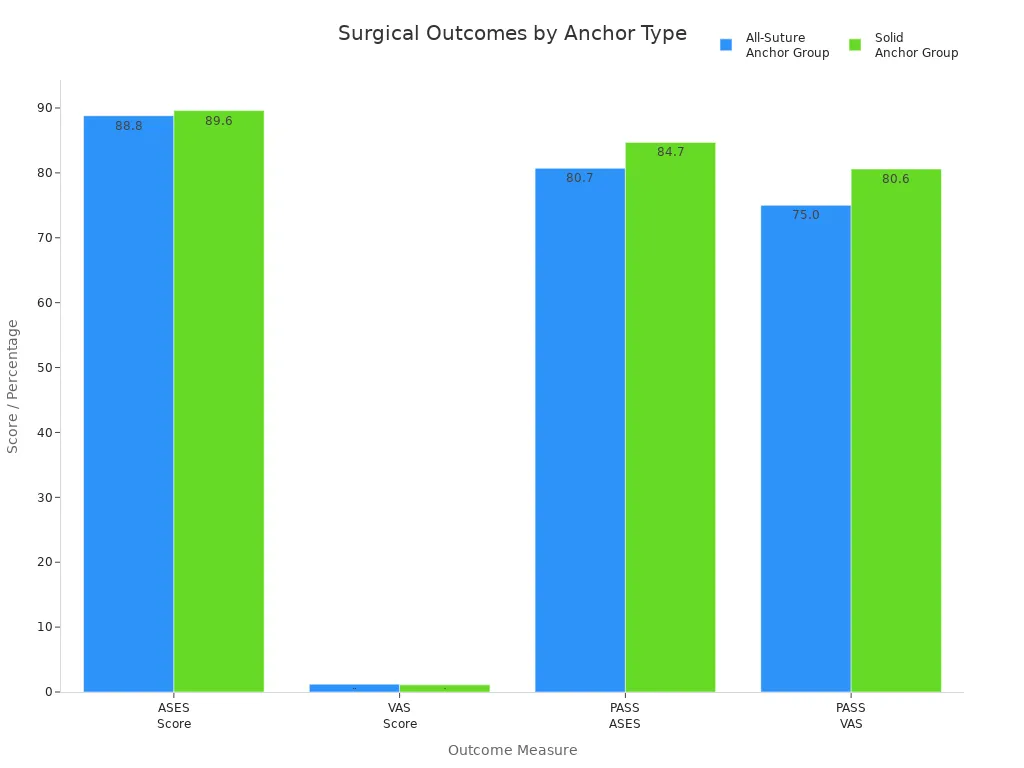
Doctors pick suture anchors because they help people get better results. You can see this in how patients score after surgery.
Outcome Measure | All-Suture Anchor Group | Solid Anchor Group | P-Value |
ASES Score | 88.8 ± 16.7 | 89.6 ± 17.8 | 0.44 |
VAS Score | 1.2 ± 2.1 | 1.1 ± 2.1 | 0.37 |
PASS ASES | 80.7% | 84.7% | 0.44 |
PASS VAS | 75.0% | 80.6% | 0.83 |
You can trust that suture anchors keep soft tissue on the bone. They help you heal and get back to your activities.
Safety and Reliability
Are Suture Anchors Safe?
You might wonder if suture anchors are safe for you. Doctors use these devices because they follow strict safety rules. Companies check each anchor with many tests. This makes sure the anchor will not break during surgery. Your doctor uses anchors made from strong things like titanium, stainless steel, or special plastics.
Suture anchors hold your tissue in place while you heal. Most people do not have problems after surgery. Doctors look for rare issues, like loose anchors or reactions in the joint. Safety checks happen all the time, from making the anchor to putting it in your body.
Tip: Ask your doctor what kind of anchor they use and how it helps you get better.
Longevity and Complications
Suture anchors can stay in your body for a long time. Some anchors dissolve over months, but others stay forever. Doctors pick the best anchor for your injury and healing. Most anchors work well for many years.
Sometimes, problems can happen. You should know what to watch for after surgery. Common problems are:
Pull-out complications
Arthritis
Osteolysis
Chronic infections
Sinus tract formation
Glenohumeral arthropathy
Doctors also see rare problems, like:
Glenoid osteolysis
Synovitis
Chondrolysis
Loose metal anchors can hurt your joint badly. About 38% of people with loose anchors had serious joint damage. One person got a wound infection after surgery. In one study, all eight people needed another surgery because the anchor failed.
Anchor arthropathy is a long-term problem after shoulder surgery. This happens when the anchor touches the joint and hurts the cartilage. Tell your doctor if you feel pain, swelling, or cannot move well after surgery.
Doctors have made anchors better to lower these risks. New anchors have fewer problems. But mistakes during surgery can still cause anchor failures. Surgeons get special training to help avoid these mistakes.
Technological Advancements
You get help from new technology in suture anchors. In 2023, more than 60 new models came out. Many use materials like PLA and PGA that dissolve in 6 to 12 months. This means you may not need another surgery to remove them.
Some new ideas include:
SmartThread anchors that remember their shape and make surgery 18% faster
Hybrid anchors that mix titanium and dissolving materials, lowering suture slippage by 24%
Knotless anchors, which are over 35% of new products, make surgery easier and 30% faster
Drug-eluting anchors that give antibiotics for 4 to 6 weeks, lowering infection by 40%
Adjustable-length anchors that help fix more than one spot, improving success by 22%
Prototype wireless anchors that send real-time data to surgeons
Here is a table showing some new anchor types and their benefits:
Innovation Type | Description | Benefits |
Knotless Suture Anchors | No need for knot-tying during surgery | Faster procedures, less risk of knot failure |
All-Suture Anchors | Small, soft, and knotless, preserve bone and tissue | Lower pressure, less chance of arthritis, better biocompatibility |
Biocomposite Anchors | Made from PLGA, β-TCP, and calcium sulfate | Stable fixation, promotes bone growth, reduces inflammation |
Future Directions | New materials for better suture chain mechanics | Stronger fixation, better healing, improved long-term outcomes |
New suture anchors are more stable when you move. All-suture anchors are stronger and stiffer than old ones. Doctors see less bone reaction and fewer gaps with these new anchors.
Note: Ask your doctor about the newest anchor choices. New designs may help you heal faster and lower your risk of problems.
You get help from suture anchors because they make healing faster. They also keep repairs strong. New research shows these anchors are very strong. They do not hurt the bone much. They have a small shape, so they do not bother you after surgery.
Benefit/Feature | Description |
Biomechanical Properties | Gives strong support for healing |
Decreased Bone Damage | Causes less harm to bone during surgery |
Low-Profile Design | Makes less irritation after surgery |
Material Composition | Safe, does not show on X-rays, and lasts a long time |
Clinical Outcomes | Helps most people heal well |
You should listen to your doctor after surgery. Tell your doctor if you feel pain or swelling. When picking a company, look for good quality and new ideas. Make sure they follow safety rules. XC Medico gives safe and trusted products for you.
FAQ
What should you expect after suture anchor surgery?
You may feel mild pain and swelling. Your doctor will guide you through recovery. You should follow instructions for rest and movement. Most people return to normal activities within weeks.
Can you feel suture anchors inside your body?
You will not feel suture anchors. They stay hidden in your bone. You may notice improved movement as you heal.
How long do suture anchors last?
Suture anchors can last for years. Some dissolve over time. Your doctor will choose the best type for your injury and healing needs.
What signs should you watch for after surgery?
Watch for pain, swelling, redness, or trouble moving. If you notice these signs, contact your doctor. Early care helps prevent problems.
Tip: Always follow your doctor’s advice for the best recovery.
Question | Quick Answer |
Can you exercise soon? | Ask your doctor first. |
Are anchors safe? | Yes, they meet standards. |
Will anchors affect X-rays? | Most do not show up. |
English
Русский
简体中文
繁體中文
العربية
Français
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
සිංහල
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu